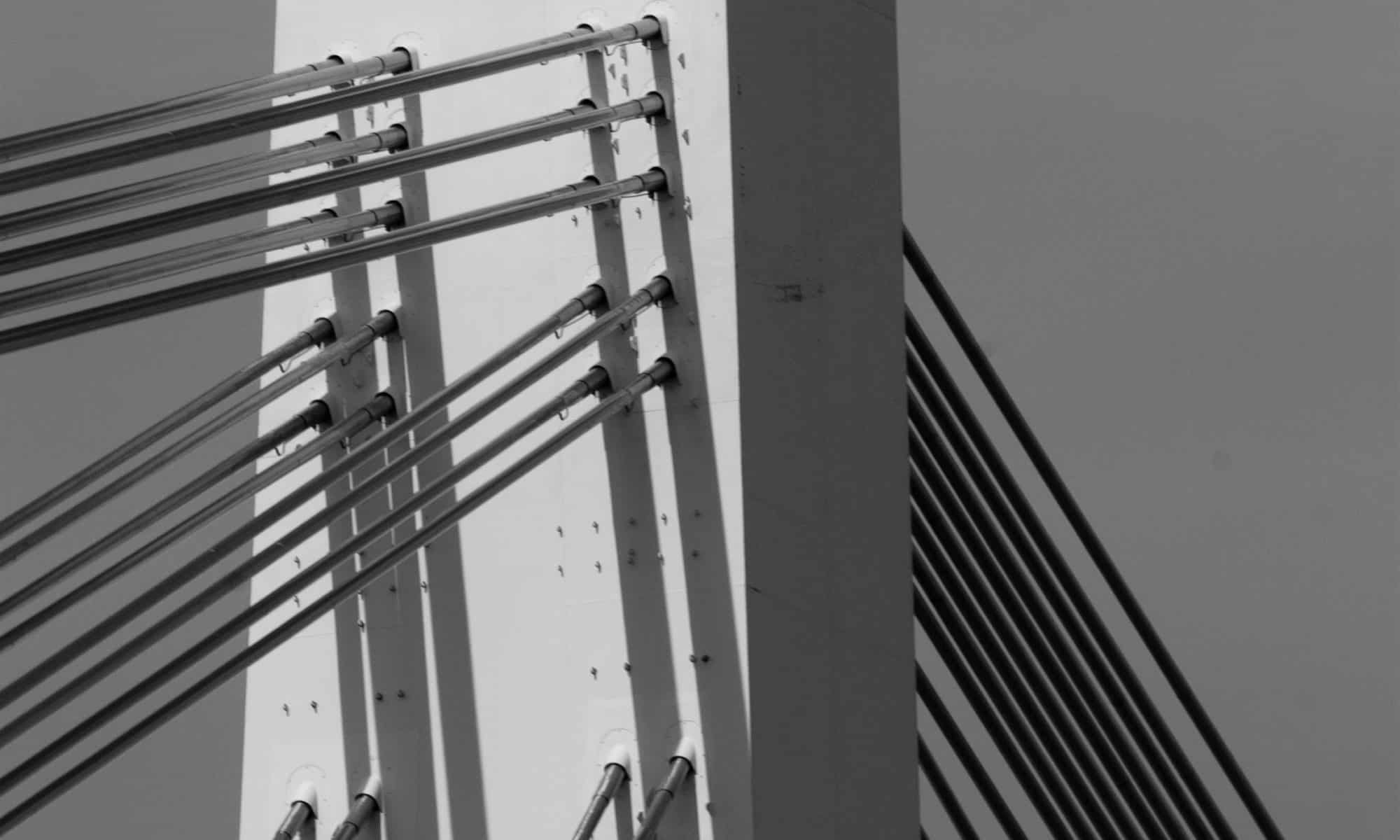
What is beacon probing?
In my recent blog article “ESX physical uplink resiliency” I’ve discussed countermeasures to harden vSphere traffic against downstream physical failures. Today I will discuss another failover detection method which can handle uplinks that are not yet dead but not functional either.
Reasons for failure can be driver / firmware related errors on the NIC itself, or a broken downstream path (cable / switch).
Beacon probing
Beacon probing is a mechanism, where an ESX host will send out beacon packets over every uplink port every second to verify that each other uplink is reachable.
![]()