Earlier this month I had the opportunity to participate in the VMware Exclusive Blogger Early Access Program. This is where VMware experts share news and upcoming features for products before the actual release date.
I would like to thank Pete Kohler and John Nicholson for the feature briefing on the release of vSAN 8 Update 2. I’d also like to thank Heather Haley from VMware’s global communications team and Corey Romero for helping to make it happen.
[This blogpost was under embargo until 22nd of August 5:00 AM PDT (14:00 CEST)]
VMware vSAN 8 Update 2 delivers a range of new features and improvements in flexibility, performance and ease of use.
New ESA Features at a glance
- vSAN ESA storage-only clusters with vSAN Max
- VMware Cloud Foundation Support for vSAN ESA in VCF 5.1
- vSAN file services now available on vSAN ESA
- New ESA Ready Node Profiles for small environments
- Support for a new class of read intensive storage devices
- Auto policy remediation
- ESA Prescriptive Device Claim
- Stretched- and 2-node-cluster impovements
- Up to 500 VMs per host (vs 200 before)
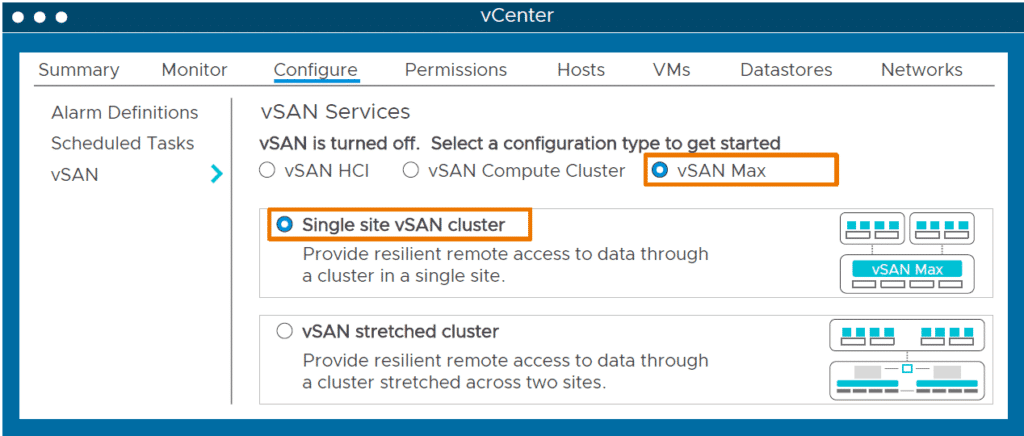
vSAN Max
One of the big new features in vSAN 8 Update 2 is the ability to completely disaggregate compute and storage by building storage-only clusters. This feature is called vSAN Max. Now you might say, “Hey, wait a minute! Didn’t we do this with vSAN Mesh? Well, yes and no. In fact, the principle is similar. You build a vSAN cluster with a lot of storage capacity and you make the datastore available to one or more client clusters. What is new is that you can now have compute-only clusters with no local disk devices and storage-only clusters with no production VMs. Also new is that vSAN Max can be consumed by vSAN clusters and vSphere clusters(!). These so-called compute-only vSphere clusters are given a minimum set of vSAN functionality that allows them to consume vSAN Max storage. No legacy protocol such as iSCSI or NFS is required to mount a vSAN Max datastore.
Source: VMware
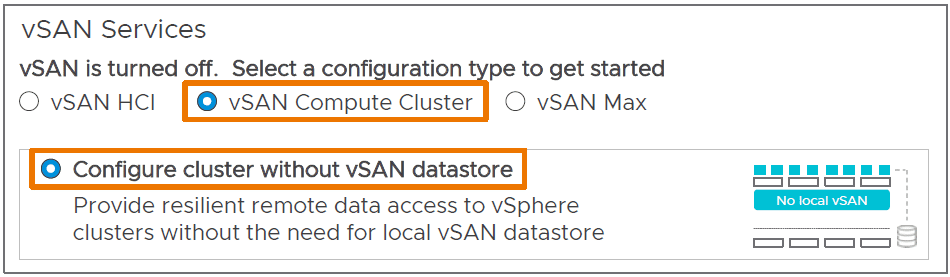
A vSAN Max is a dedicated storage cluster that can be single sided or stretched. When creating a new Cluster, you are presented with 3 options to choose from:
- vSAN HCI – This is a traditional vSAN Cluster
- vSAN Compute Cluster – A vSphere Cluster with a thin layer of vSAN to consume vSAN Max datasores.
- vSAN Max – A storage-only cluster
Source: VMware
vSAN Max Licensing
Existing vSAN editions (Standard, Advanced, Enterprise) will not include vSAN Max. There will be a new per-TiB (240 Byte) licensing model based on storage capacity rather than hosts or sockets.
vSAN Max Specs, Requirements and Limitations
- Minimum of 6 nodes per cluster with at least 150 TiB per node
- up to 360 TB per node
- up to 24 nodes per cluster
- up to 8.6 PB capacity per cluster
- ESA only – OSA not supported
- requires vSAN Max certified ReadyNodes
- Greenfield only – no migration path from other vSAN Editions
- single sided or stretched cluster
vSAN Max Use Cases
“Why would I want to take advantage of this new offer?”
The most common use cases might be third-party licensing requirements where you want to keep the number of CPU socket licences as low as possible while your application requires a lot of datastore capacity. With a standard vSAN approach, you’d have to scale out hosts to get the storage capacity you need. This will increase your socket count and third-party licensing costs.
A second use case could be form factor constraints where the number of possible disk devices per host is very limited. Consider using vSAN Max as primary storage for blade systems.
In addition, you can use vSAN Max as a central shared storage solution for the entire data centre. By incrementally adding more nodes to vSAN Max, you can easily scale such centralised storage without worrying about host or socket licensing. The licensing model is capacity based.

