Seit vSphere Version 4.1 gibt es vStorage APIs for Array Integration (VAAI), eine sehr nützliche Schnittstelle um VM Funktionen und Storage Management an die darunter liegende Hardware des Storage Array zu delegieren.
Was sind die VAAI Funktionen?
- Atomic Test & Set (ATS) – Verbessertes Verfahren zur LUN Reservierung im Vergleich zu SCSI Reservations.
- Clone Blocks, Full Copy, XCOPY – z.B. Ableitung einer VM vom Template wird an das Storage Array delegiert
- Zero Blocks – Füllen von Disk Bereichen mit Nullen
- Thin Provisioning
- Block Delete
VAAI abschalten
Es gibt Fälle, da ist es notwendig die VAAI Funktion zu deaktivieren. Zum Beispiel dann, wenn die Storage Hardware VAAI nicht, oder nicht vollständig unterstützt. Dann kann es unter Umständen zu negativen Leistungseffekten kommen.
vSphere Client
- Ansicht Hosts and Cluster auswählen
- ESX Host markieren und zum Konfigurations Tab wechseln.
- Software > Advanced Settings (Erweiterte Einstellungen)
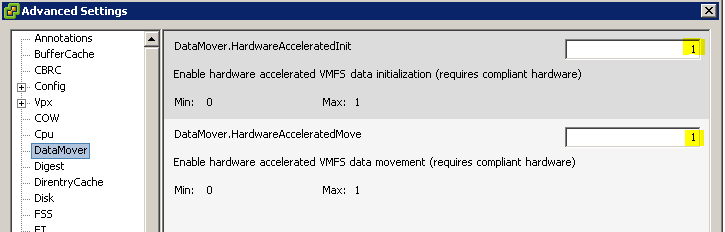
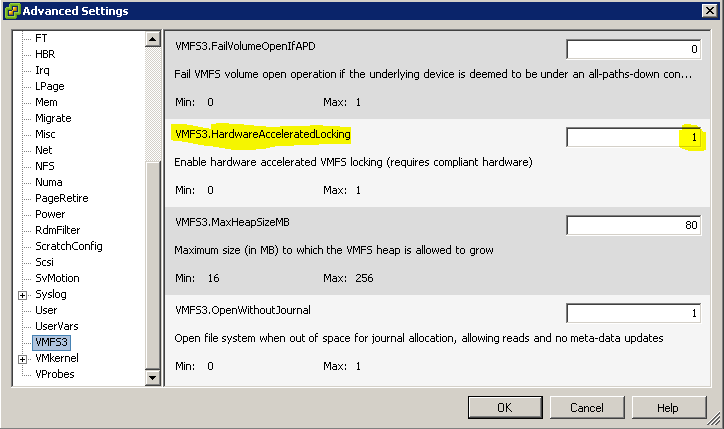
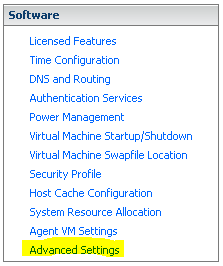 DataMover auswählen und die Werte für DataMover.HardwareAcceleratedMove und DataMover.HardwareAcceleratedInit jeweils auf 0 setzen.
DataMover auswählen und die Werte für DataMover.HardwareAcceleratedMove und DataMover.HardwareAcceleratedInit jeweils auf 0 setzen.
vSphere CLI
Im folgenden ist [connection] die Verbindungsdaten zum ESXi Server:
--server myserver.domain.com --user root --password mypassword
vicfg-advcfg [connection] -s 0 /DataMover/HardwareAcceleratedMove vicfg-advcfg [connection] -s 0 /DataMover/HardwareAcceleratedInit vicfg-advcfg [connection] -s 0 /VMFS3/HardwareAcceleratedLocking
Befehl für alle ESXi Hosts wiederholen.
Überprüfung der Einstellungen:
vicfg-advcfg [connection] -get /DataMover/HardwareAcceleratedMove
PowerCLI
Hierbei ist „Hostname“ der Name des ESX-Hosts. Der Befehl muß für alle ESXi Hosts wiederholt werden.
Set-VMHostAdvancedConfiguration -VMHost Hostname -Name DataMover.HardwareAcceleratedMove -Value 0 Set-VMHostAdvancedConfiguration -VMHost Hostname -Name DataMover.HardwareAcceleratedInit -Value 0 Set-VMHostAdvancedConfiguration -VMHost Hostname -Name VMFS3.HardwareAcceleratedLocking -Value 0
Überprüfung der Einstellungen:
Get-VMHostAdvancedConfiguration -VMHost Hostname -Name DataMover.HardwareAcceleratedMove Get-VMHostAdvancedConfiguration -VMHost Hostname -Name DataMover.HardwareAcceleratedInit Get-VMHostAdvancedConfiguration -VMHost Hostname -Name VMFS3.HardwareAcceleratedLocking
Links
vmware KB1021976 – vStorage APIs for Array Integration FAQ
vmware KB1033665 – Disabling the VAAI functionailty in ESX/ESXi (Achtung! Fehler in powerCLI commands)

Hi,
We’re having disk latency issues when performing cloning and other such like activities during the day. Usual scenario, we need to get something cloned or migrated and the task gets to around 11% and stays there for a while. Phone goes, users complain about their Outlook not responding, task abandoned.
We have a Fujitsu Eternus S1. and my question is, if we disable VAAI then what are the farther reaching connotations of doing so? This website states:
What are the functions VAAI?
Atomic Test & Set (ATS) – An improved method of LUN reservation compared to SCSI Reservations.
Clone block, Full Copy, XCOPY – eg, placement of a VM from the template will be delegated to the storage array
Zero block – filling disk sectors with zeros
Thin Provisioning
Block Delete
Will we lose all of this if we disable the VAAI function?
Thanks!
Hi
If you have an Eternus S1, you won’t benefit from VAAI anyway. So there is (from my point of view) no reason to keep it enabled.
Did you read this post too?
http://www.elasticsky.de/2012/09/vsphere5-vaai-causes-havoc-on-fujitsu-eternus-dx90/
Meanwhile Fujitsu has released a firmware (V10L68), that deals with the problem mentioned above.
But if you’re unsure what to do, please ask your local Fujitsu Storage support staff. My advice is only based on personal experience and talks to Fujitsu support members.